Note
The following documentation closely follows the paper:
Loss protection in pairs trading through minimum profit bounds: a cointegration approach by Lin, Y.-X., McCrae, M., and Gulati, C. (2006)
Simulation of Cointegratred Series
This module allows users to simulate:
AR(1) processes
Cointegrated series pairs where the cointegration error follows an AR(1) process
Cointegration simulations are based on the following cointegration model:
where \(\varepsilon_t\) and \(e_t\) are AR(1) processes.
The parameters \(\phi_1\), \(\phi_2\), \(c_1\), \(c_2\), \(\sigma_1\), \(\sigma_2\), and \(\beta\) can be defined by users. The module supports simulation in batches, which was shown in the example code block.
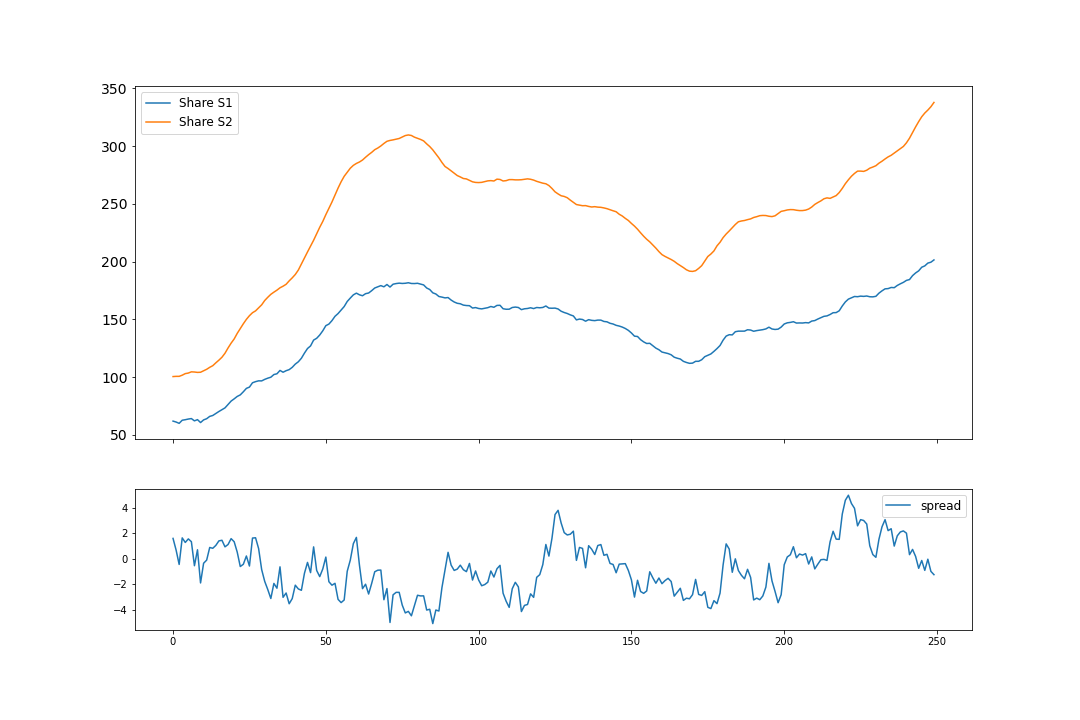
An example showcasing the cointegration simulation result. The parameters used are as follows.
Implementation
Example
# Importing packages
from arbitragelab.cointegration_approach.coint_sim import CointegrationSimulation
# Generate 50 cointegrated time series, each of which has 250 data points
coint_simulator = CointegrationSimulation(50, 250)
# Setup the parameters for the AR(1) processes and cointegration coefficient, beta
price_params = {
"ar_coeff": 0.95,
"white_noise_var": 0.5,
"constant_trend": 1.5}
coint_params = {
"ar_coeff": 0.9,
"white_noise_var": 1.,
"constant_trend": 0.05,
"beta": -0.6}
coint_simulator.load_params(price_params, target='price')
coint_simulator.load_params(coint_params, target='coint')
# Perform simulation
s1_series, s2_series, coint_errors = coint_simulator.simulate_coint(initial_price=100.,
use_statsmodels=True)
# Verify if the simulated series are cointegrated and the cointegration coefficient is equal to beta
beta_mean, beta_std = coint_simulator.verify_coint(s1_series, s2_series)
# Plot an example of the simulated series and their corresponding cointegration error
coint_sim_fig = coint_simulator.plot_coint_series(s1_series[:, 0], s2_series[:, 0],
coint_errors[:, 0])
Research Notebooks
Research Article
Presentation Slides
